The term “utility” has expanded to include not only electricity (& gas), water & sewer systems and communications services, but a hybrid of data and power transmission for low voltage devices. That’s because daily life has become more connected and more reliant upon data. With the IoT, things like Alexa, smart blinds, security camera systems, and so much more must be accessible to keep pace with the people who use them. And, that is why the role of information technology infrastructure is expanding. Advances in technology have led to a new facet of building efficiency that marries electrical systems with data and telecommunications delivery, something Versa is calling the 4th utility of building and facility design.
Some people even use the acronym MEPIT (mechanical, electrical, plumbing and information technology) and MEPI (an abbreviation of MEPIT). This post will discuss the idea of this 4th utility and its connection to Power over Ethernet (PoE).
Why Do We Need the 4th Utility?
We need the 4th utility because the infrastructure required to support the smart device is also smarter. Data transmission is more than just a wireless connection to the internet. Low-voltage PoE devices, the backbone of IoT, not only need data, but they also need power delivered simultaneously over one cable.
These installations support networks, VoIP phones, display screens, security systems, audio distribution systems, healthcare systems, robotics, and more. Though end technologies are typically installed by in-house teams, the high-voltage mains may be contracted out to security installers or audio integrators. Regulations on low voltage wiring are less strict because they pose less risk to human safety.
The point of this discussion is how the end-user arrives at their IoT infrastructure. These days, more is expected upfront in the way of building and facility design. User experience and marketplace competition play into move-in-ready installations.
As a result, Power over Ethernet (PoE) designs are becoming less of an afterthought and treated with more intentionality, becoming part of the initial design process for a building or facility.
What Systems Need The 4th Utility?
“More and more IoT connections are coming online. IoT is restructuring every aspect of a building, from construction to habitation to management. Use IoT data to make informed decisions to optimize the experience of occupants, staff and management. With asset optimization, better facilities management, and occupant safety, smarter buildings can streamline business processes and expand profits,” The Power of IoT, IBM.
At some level and in almost every case, the Internet of Things must include Power over Ethernet. To be smart, a device must implement some form of data. And, the undeniable efficiency of one-cable solutions makes it possible to keep costs down.
Smart building systems discussion:
Kitchens [lighting systems and convenience apps]
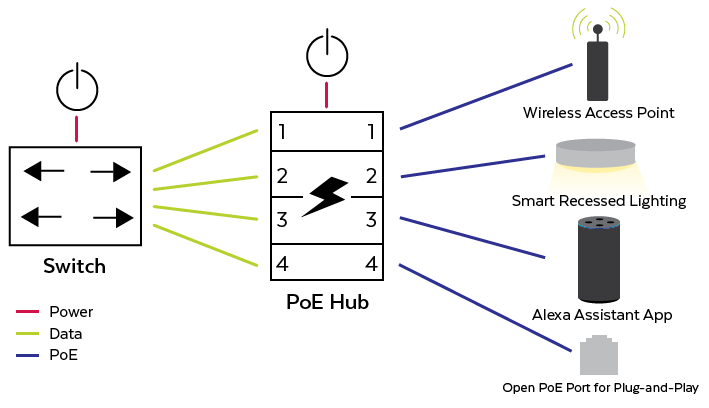
In kitchens, hubs are needed to support wireless access points, smart recessed lighting, and in the case of residential, assistant apps like Alexa or Echo. Though not everyone is on board with the assistant app, contractors and builders are laying out the support technologies to make using this equipment plug-and-play. Voice-activated controls of smart home systems offer convenience for busy people on the fly.
 HVAC Controls [tracking and controlling]
HVAC Controls [tracking and controlling]
LANs connect monitoring devices and sensors to enterprise networks and home systems through the accessibility screens. This technology allows administrators and facilities managers cross-platform visibility. Data and power make sensor installations easy. Usually, these sensors are attached to lighting systems–also powered by PoE–which automatically shutdown lights and cooling systems when areas are unoccupied.
Entertainment [display screens and telecommunications consoles]
Display screens on campus or in airport kiosks, as well as transportation schedules, install easily in convenient locations throughout public areas, using one cable for power and data. When connection points for these networks are addressed in the facility design stage, they become even more convenient, allowing for flexible relocation as these spaces evolve.
Wireless Access Points [communications]
As data-access becomes increasingly efficient, wireless infrastructure is growing in capacity and speed. High-performance IEEE 802.11a technologies can reach speeds of up to 5Gbps and beyond on 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands, connected to building networks for data and power by simple Cat6 or Cat6A Ethernet cables.
Camera Systems [power and monitoring systems]
Security surveillance cameras systems need motion-activated capabilities and high-resolution images to be effective. The motion activation ensures that memory is not burned up during no occupancy periods. Once memory reaches capacity, systems record over earlier footage. This makes backtracking more difficult and retrieval of event recordings difficult, if not impossible.
High-resolution images and proper lighting ensure that in the event of criminal activity, recorded evidence will be granular enough to be admissible in legal proceedings. Entry points, secure locations, or building access areas are more secure and high-resolution technology quickly installed when the 4th utility is already in place.
AI Insights and Data Analysis [asset tracking and data analysis]
Finally, harnessing the data that low-voltage devices gather, gives decision-makers realtime insight into the flow of occupants and how to cut waste while providing efficiency where needed.
What Buildings Use The 4th Utility?
 Commercial Buildings
Commercial Buildings
A commercial building includes a wide range of uses: the big box or department store, the warehouse or other retail space. This type of facility is considered multi-use or multi-functional.
Industrial Facilities
An industrial building may be used in a variety of industrial ways: manufacturing products, washing, repairing services, power generation and even processing livestock.
Hospitality and Convention Centers
These buildings are self-explanatory. They are large multi-use public spaces that adapt and change to meet the needs of event participants, business travelers, and vacationers.
Academic Institutions
These facilities are becoming smarter. Even those used for early childhood education are relying much more heavily on digital technology. Little ones are being introduced to computers at a much earlier age, and teachers and administrators are relying on technology to keep children safe and elevate learning opportunities.
Residential Buildings
Residential buildings, from a legal perspective, are both single-family or multi-family dwellings that are heated or mechanically cooled. They may also include nursing homes, hostels, and dormitories. When the 4th utility is pre-designed into residential structures, connecting technology becomes as simple as plugging in a cell phone charger.
Conclusion
Call it in-building internet infrastructure, call it PoE infrastructure, or IoT-ready infrastructure; the 4th utility is now an integral part of building and facility design. Having it in place and ensuring a property is move-in ready is becoming a game-changer in the commercial real estate (CRE) field.
“CRE professionals are realizing that, if they stick with the catch-up approach, they may never be done with the endless upgrade cycle,” says John Dulin in “Small Cell Network Infrastructure: Now The Fourth Utility.” (Connected)
Versa Technology would like to add, “Move-in ready is what the market expects and it’s the key to winning sales.”
Learn more about Versa Technology Networking Equipment for Every Environment.

