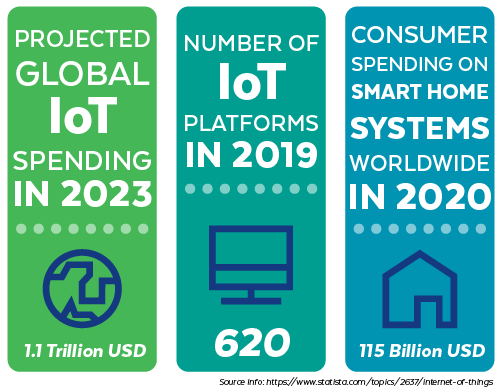
Building out an IT network or network expansion can be as fast or as gradual as your business requires. These days, network expansion is not an “if” but “when” proposition. Security Today estimates an average of 127 devices1 connect to the Internet every second. This ever-increasing rate of connectivity means that the infrastructure needed to support these technologies must be equally as swift.
Thankfully, the basic design of Power over Ethernet (PoE) networking and Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE) is quick and simple to set up and use. One device that is rising in popularity is the Ethernet Extender (also called a Network Extender or a LAN Extender). This one device gives network administrators a lot of bang for their buck, as it allows administrators to connect local area networks (LANs) to remote locals.
Ethernet extender kits enable network administrators to extend a LAN beyond its standard 100m limitation using a Registered Jack-11 (Rj11) line.
Ethernet Extenders make it possible to establish high-speed network links between distant locations such as enterprises, campuses, and other localities.
Communication is possible because of the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), which allows different network devices to share information. This protocol is useful because networks develop over time, and not all of them are the same hardware or run the same software.
At this point, let’s cover some basics.
What are Ethernet Extenders?
Let’s begin with the Ethernet.
Ethernet is the data-transmission protocol used by power devices (PDs) connected by a LAN. Ethernet technology encompasses a technique called Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSM/CD), which enables multiple PDs to share a communication channel over a single cable such as CAT5e.
Next, it is essential to know that one of the Ethernet’s few limitations is that simple PoE transmits signals up to only 100m (328 feet). Many LANs need to span much larger distances (think shopping malls, academic campuses, hotels, sports venues, etc.). Ethernet Extenders lengthen that reach to unite networks that need to travel larger distances.
Ethernet extenders utilize an assortment of transmission technologies and physical media (e.g. copper wire, fiber-optic cable, coaxial cable, wireless).
How Do Ethernet Extenders Function?
Copper-based Ethernet extenders use unconditional (without load coils) wire such as unused twisted pairs and alarm circuits. They use copper wiring that has 2-, 4-, and 8-wire alternatives to extend a LAN. Although copper wire transmission does not provide the speeds that fiber-optic does, it does allow the use of existing network-grade copper or CCTV coaxial cable wiring. Ethernet extenders are economical and have low maintenance requirements. This makes them an acceptable alternative to expensive fiber-optic cable.
Connecting a private LAN between distant locations is a challenge. Wi-Fi needs a clear line of vision, special antennas, and is affected by the weather. It may be feasible for distances up to 200m (656 feet) to set up an ordinary Ethernet bridge or router in the middle.
With the use of Very High-Speed Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) technology, two LANs are connected over a single twisted pair of wires. Connections of 300m (1,000 feet) at 100Mbps symmetrical or up to 5 miles or more at 128 kbps is achievable.
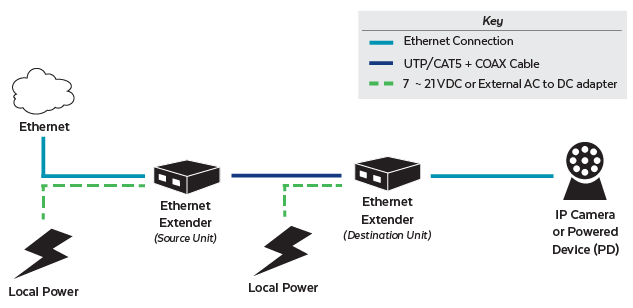
How Do You Set Up an Ethernet Extender?
Most Ethernet extenders are plug-and-play, so set up is easy.
- First, you will need to setup one of your Ethernet Extenders to operate as the Source unit.
- Power on both units by connecting the power adapters into the wall.
- Then, connect the power to one of your Ethernet Extenders from your Ethernet Extender Kit.
- Plug the Ethernet cable into any of the ports on the back of the Unit. Connect the same Ethernet cable to your Ethernet Switch.
- To Set your device to operate as a source, flip the dip switch to OT or office terminal mode. The RT LED indication will turn off.
- Then connect your telephone cable to the wall.
- Connect the adjacent side of your telephone cable to the VDSL2 interface located on the front of the unit.
You will then need to setup your remaining Ethernet Extender to operate as the destination unit. To set the device to operate as the destination, flip the dip switch to RT or Remote Terminal mode. The LED RT indicator will turn on.
- Plug your Ethernet cable into any of the ports on the back of the unit.
- Plug the adjacent side of the Ethernet cable to your powered device such as a wireless access point.
- Connect your telephone cable to the VDSL2 interface located on the front of the unit. Connect the adjacent side of your telephone cable to the wall. The link light will continuously flash and turn solid once it successfully synchronizes with the other unit.
Versa Technology Ethernet Extenders
Ethernet extender kits from Versa Technology can easily extend a network up to at least 9,000ft (approximately 1.7 miles). These products support high-speed connectivity without any additional copper wiring. Versa Technology offers Ethernet extender kits for every networking environment.

Our VX-VEB160G4 Ethernet Extender Kit has the following features:
- Interface: 4 x 10/100/1000Base-T, 1 x VDSL2
- Speed DS/US: Up to 190Mbps/Up to 110Mbps
- Power Supply: 12VDC over 2.1mm DC Jack
- Power Consumption: 4.5 Watts Max
- Operating Temperature: -20 degrees C to 65 degrees C
- Standard: IEEE 802.3 compliant
- Distance: Up to 9,000 feet

Versa Technology’s VX-700LRP-KIT is a single-port, long-reach industrial Ethernet extender kit that features:
- Network Connector: 10/100/1000 Mbps
- Operating Temperature: -40 degrees to 75 degrees C
- Type: End-Span (CO)/Mid-Span (RT)
- Standard: 802.3at
- Max. PoE Power Budget: 30 watts
- Distance: Up to 3,900 feet
- Power Requirements: 48-57V DC
A Word About PoE+
The difference between PoE and PoE+ is power.
The original PoE standard (IEEE 802.3af) delivers up to 15.4 watts of DC power to a device. Since the development of this standard, a whole new generation of devices that require higher levels of power has evolved.
PoE+ (IEEE 802.3at) is the latest standard and provides up to 25.5 watts using CAT5e/6 UTP cable. PoE+ is needed to support devices such as Pan/Tilt/Zoom cameras, video IP phones, and alarm systems.
Our PoE Ethernet extenders are simple play-and-plug devices that support various distances, are IEEE-compliant, and can be daisy-chained to support longer spans.
Conclusion
Upgrading a LAN with a new system that communicates using Internet Protocol (IP) technology is an expensive and monumental task. And changing the wiring infrastructure can be even more costly and time-consuming.
The use of Ethernet extenders is the solution to this problem. They provide Ethernet connectivity over existing coaxial cable and even over old legacy telephone/communication cable.
The use of Ethernet extenders is simple, vastly more cost-efficient, and extends the life of your wiring infrastructure.
Visit here for announcements, featured products, and video tutorials. For help choosing the right Ethernet Extender kit for your network implementation, you can contact us here.
———
Source
- https://securitytoday.com/articles/2020/01/13/the-iot-rundown-for-2020.aspx